China, the world’s largest emitter of greenhouse gases, is on the way of a significant shift in its carbon emissions trajectory. According to recent analyses, China’s carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions are set to fall in 2024 due to Record Growth in Clean Energy. This change is due to the Net Zero Emission Plan & massive growth in the installation of new low-carbon energy sources.
China’s Co2 Emissions Growth and Decline
China’s CO2 emissions have been on a rebound since the end of the nation’s “zero-Covid” period, rising by an estimated 4.7% year-on-year in the third quarter of 2023. The strongest growth was observed in oil demand and other sectors that had been affected by pandemic policies, until the lifting of zero-Covid controls at the end of 2022.
Despite a recovery in manufacturing, record levels of wind and solar power output, along with a faster than expected growth in electric vehicles, are predicted to reduce overall emissions.
Why is the renewables industry in China growing so fast?
China’s 2020 declaration that it will achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 sent a strong political message in support of renewable energy investments and Net Zero Emission Target.
There were additional macroeconomic influences at work. According to Lauri Myllyvirta, principal analyst at the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA), an investigation on aggressive real estate loans since 2020 has coincided with pandemic-era stimulus measures that helped in encouraging greater investment into the manufacture of renewables.
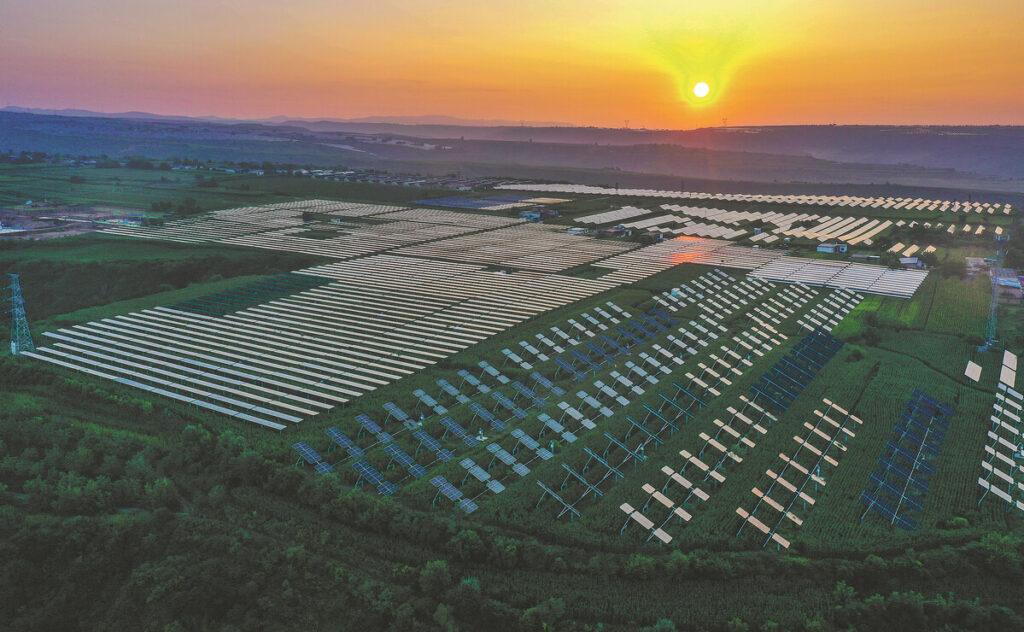
This year, financing to the manufacturing sector has increased significantly, especially in the high-tech and green industries.
Rapid economic growth of China
China’s Solar, wind and hydropower Growth in 2024
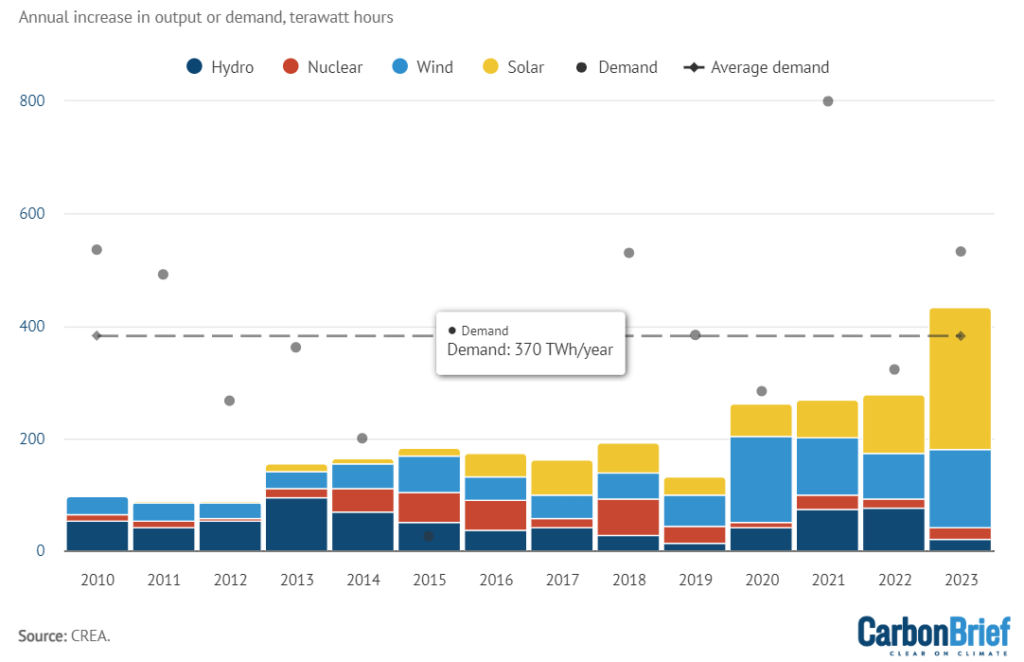
Even though emissions increased in 2023, there was a historically significant increase in the number of low-carbon energy projects. Solar power has seen the most notable rise; projected installations in 2023 are predicted to reach 210 gigawatts (GW), which is approximately twice the installed capacity of solar power in the US and four times what China added in 2020.

An estimated 423 terawatt hours (TWh) will be produced annually by the newly constructed solar, wind, hydro, and nuclear capacity added in 2023 alone. This amount is equivalent to France’s annual electricity consumption.
Due in major part to China’s “Whole County Solar” approach, which involves holding a single auction to cover a specific percentage of the rooftops in a county, around half of the solar panels added this year will be installed on rooftops.
In total, China projected to add 210GW of solar, 70GW of wind, 7GW of hydro, and 3GW of nuclear power in 2023. The predicted power generation, assuming newly added capacity operates in line with the current company, is displayed in the table below.
| Source | GW | Average utilization | Tera Watt |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar | 210 | 13.6% | 251 |
| Wind | 65 | 23.0% | 130 |
| Nuclear | 3 | 83.4% | 21 |
| Hydro | 7 | 36.7% | 21 |
| Total | 284 | 17.0% | 423 |
In 2023, clean energy growth will exceed average demand growth for the first time
Frequently Asked Questions
What is China’s energy consumption in GW?
China has 2.92 TW of installed power generation capacity in 2023, of which 1.26 TW is renewable and consists of 376 GW of wind and 425 GW of solar power. The remaining capacity, 1040 GW in 2019, was primarily coal-based. Also nuclear plays an increasing role in the national electricity sector.
What is China’s CO2 emission plan?
China is expanding its installed renewable capacity at a rate and scale that is incomparable in a world where countries are failing to meet their climate commitments. For example, China promised in 2020 to more than double its current capacity of 1,200 gigawatts of renewable energy by 2030.
What is China’s Net Zero emission plan?
“Dual carbon” goals are the two climate goals that China has set, as declared by President Xi Jinping in September during the 75th session of the United Nations General Assembly in 2020.
President Xi announced that China would reach its carbon emissions peak before 2030 and become “carbon neutral” before 2060.
Also Read:
Rapid economic growth of China
Most Powerful Countries in the World(2024)
Data Source & Conclusion
The National Bureau of Statistics, Carbon Brief, National Energy Administration, China Electricity Council, China Customs, and WIND Information, an industry data provider, are the sources of the data used in the analysis.
As per the reports, China became a Super Power in Green Power Sector ahead rest of the World. We should learn the good things here and accelerate our own country Green Revolution.
Hope this Article have provide you some information, then please Share and Comment.

Informative post