The world of semiconductors is buzzing, and India is quickly becoming a major player. Many people are excited about this sector, especially since it has seen huge growth in the United States. They hope for similar success in India. This hope is neither completely right nor completely wrong. To understand why, you must first know what a semiconductor is, how it’s made, and which Indian companies are involved in its different stages of development.
Just like the car industry has car makers, battery companies, and fuel suppliers, the semiconductor sector has many different types of companies. Each company plays an important, but different, role. This post is the first part of a two-part series. It will cover 5 important Indian companies that work directly with semiconductors or are growing their presence in this field.
What is a Semiconductor?
Imagine the processor in your computer or phone. It has millions, or even billions, of tiny switches. These switches are called transistors. A transistor can either be on or off. Computers understand only “zeros” and “ones,” which means “off” or “on.” We communicate with a computer, and it performs tasks, by using different “on” and “off” combinations of these tiny transistors.
Transistors are made from semiconductors, usually silicon. They are called “semiconductors” because you can control when electricity passes through them. Think of it this way:
- Conductors (like copper) always let electricity pass.
- Insulators (like rubber) never let electricity pass.
- Semiconductors are in between. You can control their ability to conduct electricity.
This special, controllable nature makes semiconductors perfect for building transistors. So, semiconductors make transistors, and billions of transistors make up your CPU or GPU.
Semiconductors do more than just make processors. They are also used in:
- LED lights and displays
- Solar cells
- Sensors (like in your phone’s fingerprint scanner)
- Medical equipment (like MRI machines)
- Wi-Fi routers
- Satellites (which use semiconductor lasers)
- Defense and aerospace industries
Semiconductors are truly everywhere in modern technology.
How Semiconductor Chips are Made
Making chips is a very complex process. Billions of tiny transistors must fit into a small chip, and the final product must work perfectly. This involves several key stages. Understanding these stages will help you see where different Indian companies fit into the overall process.
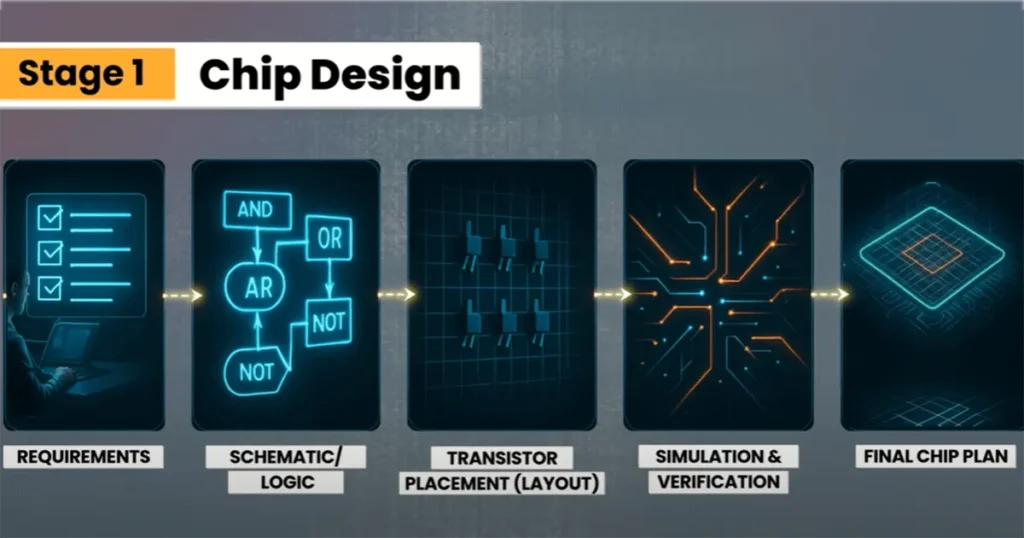
Stage 1: Chip Design
This is where the blueprint for the chip is created. Computer engineers use special software to design the chip. They decide where the transistors will go and how the electronic circuits will allow current to flow. They also define what the chip’s job will be.
Stage 2: Wafer Manufacturing
This stage creates the silicon wafers. These are very pure, thin slices of silicon, which comes from sand. First, silicon is melted and turned into a very pure liquid. Then, it is crystalized into large, solid blocks called ingots. Finally, these ingots are cut into thin slices, which are the silicon wafers.

Stage 3: Fabrication
This is the longest and most important part of the process. In fabrication, circuits are printed onto the silicon wafer, and transistors are built. It involves several steps:
- Photolithography: The circuit design is transferred onto the wafer using UV light.
- Etching: Unwanted areas of the material are removed.
- Doping: Controlled amounts of impurities are added to improve how well the material conducts electricity.
- Metallization: Metal layers are added to allow electricity to flow within the chip.
During this stage, transistors, resistors, and capacitors are all created and connected. This ensures the semiconductor works exactly as it was designed. Fabrication is the most difficult, complex, and valuable part of chip making. Companies involved in this stage often earn the most money.

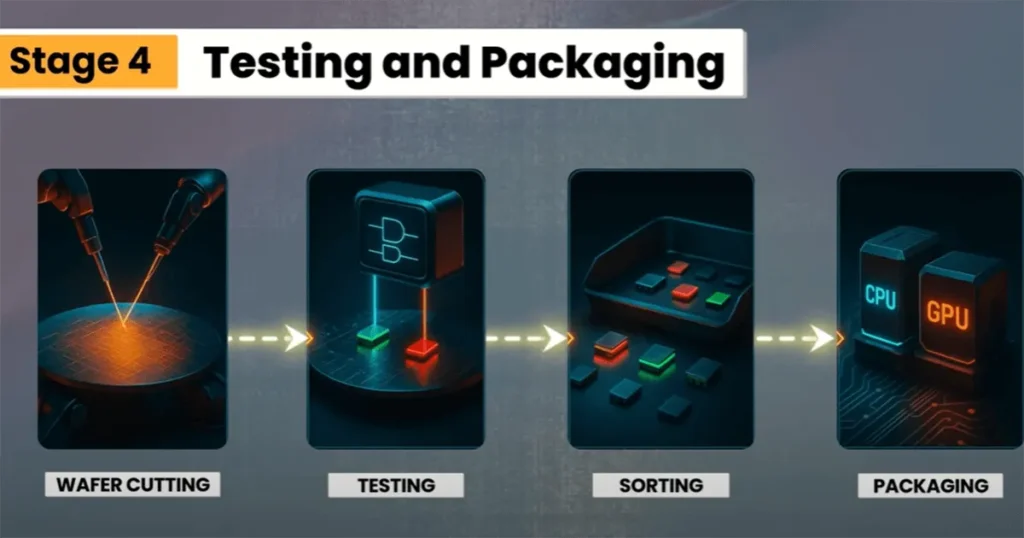
Stage 4: Testing and Packaging
After fabrication, the wafer is cut into individual chips. Each chip is then tested to find and reject any faulty ones. The chips that pass these tests are then packaged. This prepares them for their final use in electronic devices.
Currently, no single company in India handles all four stages. However, several Indian companies are involved in different parts of this process. Some are pure semiconductor companies, some are support companies, and others are growing their focus on the semiconductor sector.
Key Indian Companies in Semiconductors
Now, let’s look at six Indian companies and their roles in the semiconductor world.
1. MosChip Technologies

MosChip Technologies is a fabless semiconductor company. This means they design chips but do not manufacture them. They create various types of chips:
- ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits): These chips do one specific task, like encrypting data for a Wi-Fi router.
- SoCs (System-on-Chips): These chips include an entire system on one piece of silicon, such as a mobile phone processor with a CPU, GPU, and other interfaces.
MosChip also designs devices for the Internet of Things (IoT), embedded systems, and other electronic products. These serve sectors like aerospace, defense, telecom, consumer electronics, and healthcare. In simple terms, MosChip acts like a chip architect, creating the blueprints that other manufacturers then build. They focus on the design stage of the semiconductor value chain.
MosChip is a small-cap company with a market value around 3,000 crore rupees. It has shown strong growth, with sales growing 36% per year over the last five years. Profits have also grown well. However, its stock has risen significantly, leading to a high price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio of 79. While high, this P/E could be justified if the company continues its strong sales and profit growth.
It’s challenging to predict MosChip’s future because they do not release quarterly investor updates or hold conference calls. Their website has limited information, and annual reports are often late. Few foreign or domestic institutional investors hold their stock. The public owns more shares than the company’s founders, which can be a concern at this stage. MosChip has performed well historically, but the lack of public data makes it a high-risk stock for future analysis. Still, for those seeking a pure semiconductor stock in India, MosChip is one to watch.
2. Kaynes Technology India

Kaynes Technology India is a mid-cap company with a market value of around 45,000 crore rupees. Kaynes is an ESDM (Electronic System Design and Manufacturing) company. This means they design and manufacture electronic systems. For example, if a car company wants to launch an electric scooter, Kaynes would design and make the electronic control boards for the scooter’s various functions. They deliver a complete, ready-to-use product to the client. The circuit boards behind functions like turning on headlights or seeing your speed on the speedometer are what Kaynes makes. They even supplied critical electronics for India’s Chandrayaan-3 mission.
While their current work is separate from semiconductors, Kaynes is now entering the semiconductor space. They are building an OSAT (Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Testing) facility, which should be ready by December 2025. This means Kaynes will be involved in the fourth stage of semiconductor chip manufacturing: assembly and testing. Once operational, this facility could add about 100 crore rupees to their revenue by late 2026, possibly making up 10-15% of their total business.
Kaynes has a very strong business. Their order book has grown from 500 crore to 75,000 crore rupees in just one year. This order book is 15 times their current revenue, which is a massive figure. Management expects a 34% growth in revenue for fiscal year 2026. The company has already been growing its sales by 49% per year over the past five years.
The stock’s P/E ratio, currently around 133, was once as high as 200. This raises questions about whether the stock is overvalued. A high P/E ratio means investors expect very high growth. While the stock corrected by 50% from its peak, it has started a new upward trend. This is due to strong growth projections, the huge order book, and their entry into semiconductors. These factors make investors optimistic despite the high P/E ratio. Kaynes is a fundamentally strong company that is expanding into the semiconductor sector.
3. ASM Technologies

ASM Technologies is a small-cap stock with a market value of around 4,500 crore rupees. Over the last five years, ASM has improved its sales, but its profits have been inconsistent. However, the last two quarters have shown strong growth in both sales and profits. This growth comes from their two main business areas: ER&D (Engineering, Research & Development) and DLM (Design-Led Manufacturing).
In their core business, ASM’s engineers design machines and develop the software that runs them for other companies. Once the design is approved, ASM can manufacture these machines in their own factories.
ASM’s connection to semiconductors is indirect. They do not make chips or test them. Instead, they design equipment for companies that make chips. They have a joint venture that creates tools and subsystems for fabrication companies. So, ASM acts as a support system for the semiconductor business, designing tools for the fabrication stage. They do not disclose how much of their revenue comes from semiconductor-related work.
The company’s existing business is growing well. They recently signed an agreement with the Karnataka government to set up two new facilities to expand their DLM business. ASM has a high P/E ratio of 116. However, if you consider only the strong performance of the last two quarters, their forward P/E ratio drops to around 68. This is because their revenue structure changed significantly.
ASM is a relatively young company with a good global presence. The sector they operate in is growing, and they are expanding their capacity. A P/E of 60-70 could be justified for the long term. However, there is a risk: if profit growth doesn’t continue in the next two quarters, the stock could face a significant drop. Investors need to be aware of this risk.
Related Post: NVIDIA-huge-profit-gain-in-fy-2024/
4. Sasken Technologies

Sasken Technologies is an engineering partner for other large tech companies. They don’t make chips or gadgets themselves. Instead, they help other companies with the design and testing of new chips, and they improve existing chips, software, and devices. Their business covers many areas, including automotive, consumer electronics, industrial, satellite communication (SatCom), and telecom. The semiconductor sector is another important segment for them.
Sasken is involved in Stage 1 (chip design) and Stage 4 (testing and validation) of the semiconductor process. They act like an architect, similar to Kaynes Technology, but also like a quality checker. Additionally, Sasken develops the software that runs on these chips.
Let’s use an example from the car industry. If a car company wants to create a self-driving feature, it needs a powerful processing chip. While a company like TSMC or Samsung would make the chip, Sasken Technologies would help design and test it. Sasken would design the analog and radio frequency (RF) parts of the chip. These parts process signals from the car’s cameras, radar, and sensors. Sasken would also test the chip in simulated environments. This ensures the chip works reliably in critical situations, such as an automatic braking system responding correctly if a child suddenly appears in front of the car. Sasken also develops the firmware and middleware software that goes into these chips. They do similar work for other sectors.
Sasken’s website and annual reports state that semiconductors, along with automotive, are their main business areas and major sources of revenue. However, the company does not disclose the exact revenue contribution from semiconductors. Sasken is serious about expanding in the semiconductor space. They recently increased investments in two of their subsidiaries to strengthen their services related to semiconductor design and foundries.
Financially, Sasken’s revenue growth has not been consistent. Revenue declined from fiscal year 2019, saw a slight improvement in 2023, then fell again, before reaching its best year in 2025 with 551 crore rupees in revenue. However, this isn’t significant growth compared to 2019. The biggest challenge for Sasken is profitability. While revenue improved last year and last quarter, the company’s profits are not growing.
Management acknowledges this problem, attributing it to increased spending on hiring skilled workers and on research and development (R&D) costs. They justify this by saying it’s necessary to build future capabilities and grow the business. Whether these efforts will lead to future profit growth remains to be seen. If the company can link revenue growth with profit growth, the stock could be fairly valued today.
5. CG Power

CG Power is the first large-cap stock on our list. Its stock has been consolidating for the past year. With a P/E ratio around 120 and profit growth of 10-11%, the stock appears overvalued. So, why are investors so attracted to it, and what is the company doing that could boost its future growth?
CG Power provides electrical and electronics infrastructure for the power, industrial, and railway sectors. They mainly make motors, transformers, switchgear, and railway electronics. This core business is performing well and growing. Sales growth has been 22% per year over the last three years, and operating profit growth is consistent. Based on these numbers, the company’s P/E ratio should be closer to 30-50 in today’s market.
The reason for its high P/E of 120 is its upcoming semiconductor business. CG Power recently announced an OSAT facility in Gujarat with a capacity of 5 lakh chips per day. They also have another new factory planned to be operational by 2027, with a capacity of 14 lakh chips per day. Additionally, CG Power acquired the Exxelia Semiconductor Group, which designs RF components. This acquisition means CG Power is now involved in two stages of semiconductor chip development: design and assembly & testing.
These recent announcements and developments are why CG Power’s share price has risen significantly. Currently, it’s hard to estimate how much the semiconductor division will contribute to their business, which makes it difficult to comment on the stock’s valuation. Analysts are divided on CG Power. The highest price target given for the stock is 890 rupees, close to its previous all-time high. It remains to be seen whether this target will be reached or if the market will reject the stock at a P/E of 120. CG Power is definitely a stock to watch.
Related Post : Top 10-tech-companies-worldwide-by-market-cap/
Conclusion
This deep dive into the Indian semiconductor sector, focusing on MosChip, SPEL, Kaynes, ASM Technologies, Sasken, and CG Power, shows a vibrant and complex industry. These companies are playing diverse roles, from chip design to assembly and testing, and even providing supporting equipment. While some are pure semiconductor players, others are strategically diversifying into this high-growth sector.
The semiconductor industry is still developing in India, offering both significant opportunities and risks. Understanding each company’s specific role, financial health, and future plans is crucial for anyone interested in this exciting space. As India continues to build its presence in the global semiconductor landscape, these companies will be key to its success.